The set of astonishing pictures from the Hubble Space Telescope – one
of the largest and most versatile orbital telescopes that has recently
celebrated its 22nd year of operation.
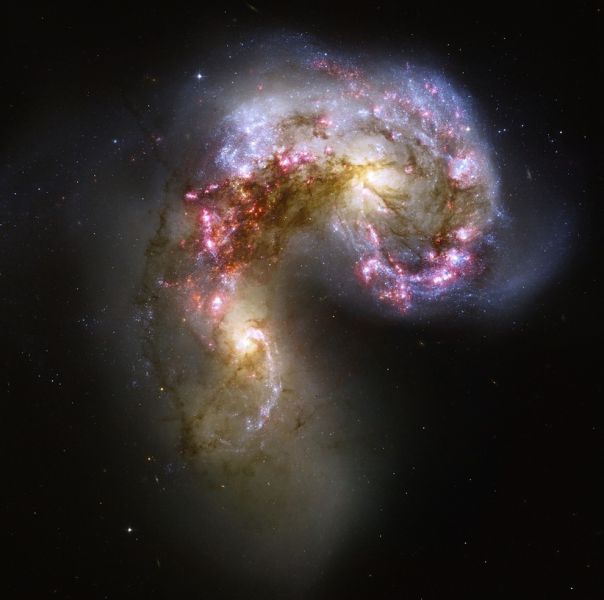

The merging Antennae galaxies. As the two galaxies smash together, billions of stars are born, mostly in groups and clusters of stars.
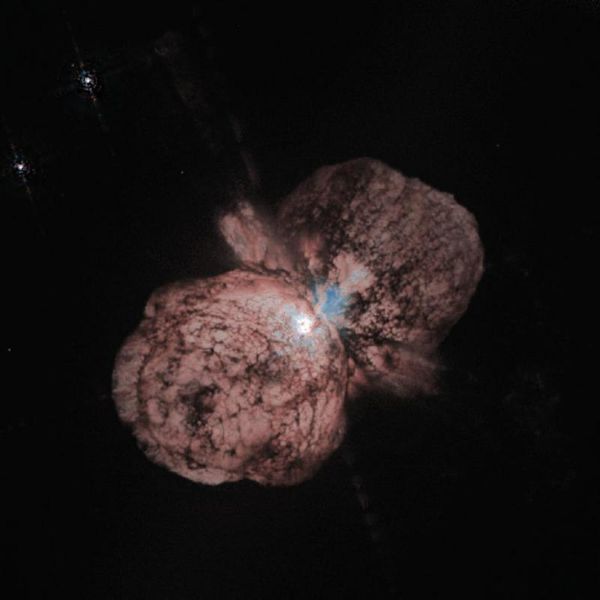
The massive star Eta Carinae in our Milky Way galaxy that experts believe might explode in a supernova at any time.
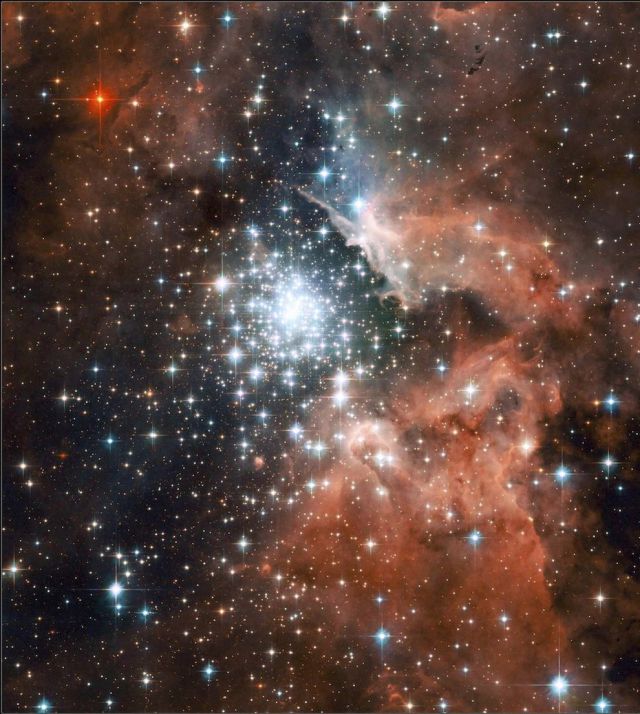

A giant star-forming nebula with massive young stellar clusters.
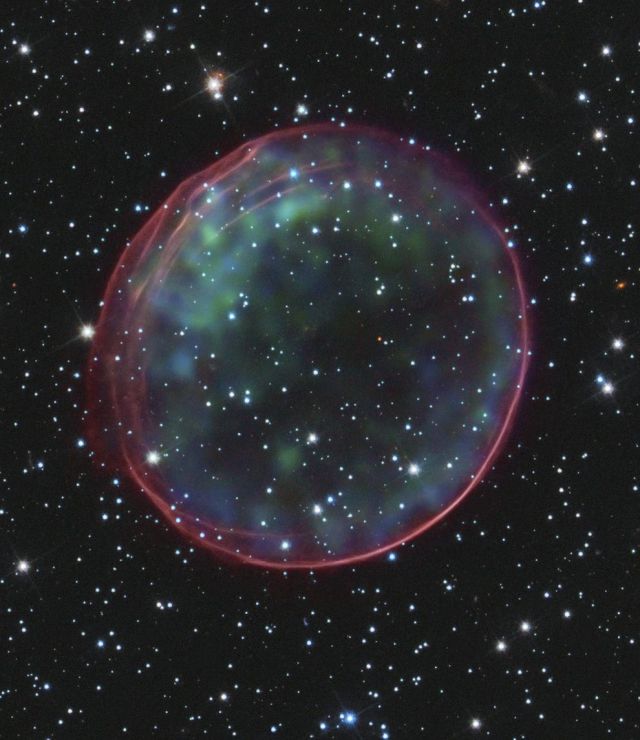

Supernova remnant 0509-67.5, located in the Large Magellanic Cloud, a small galaxy about 170,000 light-years from Earth.
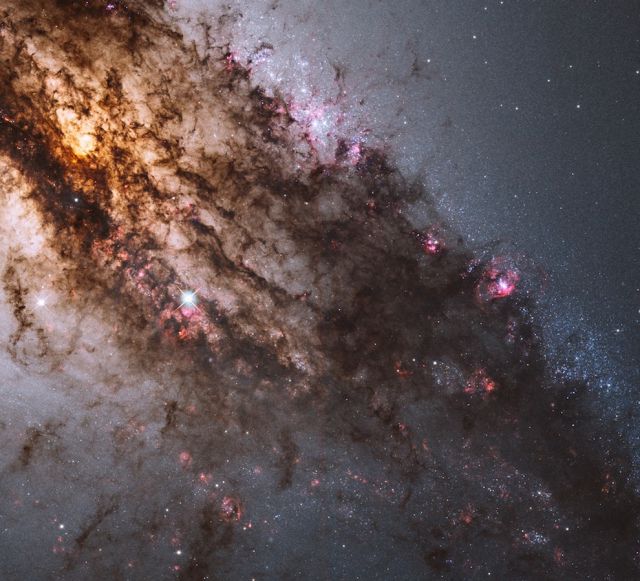

Young, blue star clusters.
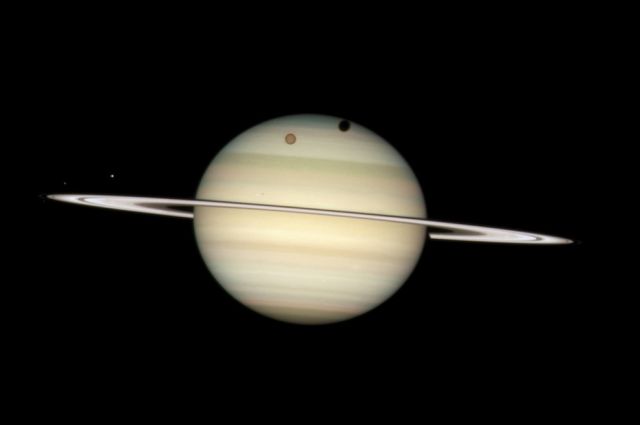

The four moons of Saturn passing in front of their parent planet. The giant orange moon Titan casts a large shadow onto Saturn's north polar hood. Below Titan, near the ring plane and to the left, is the moon Mimas, casting a much smaller shadow onto Saturn's equatorial cloud tops. Farther to the left, and off Saturn's disk, are the bright moons Dione and the fainter Enceladus.
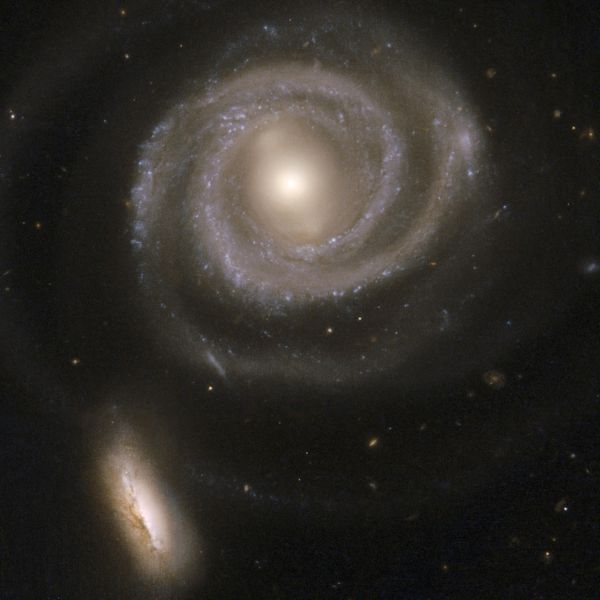

Interacting galaxies consisting of NGC 5754, the large spiral on the right, and NGC 5752, the smaller companion in the bottom left.
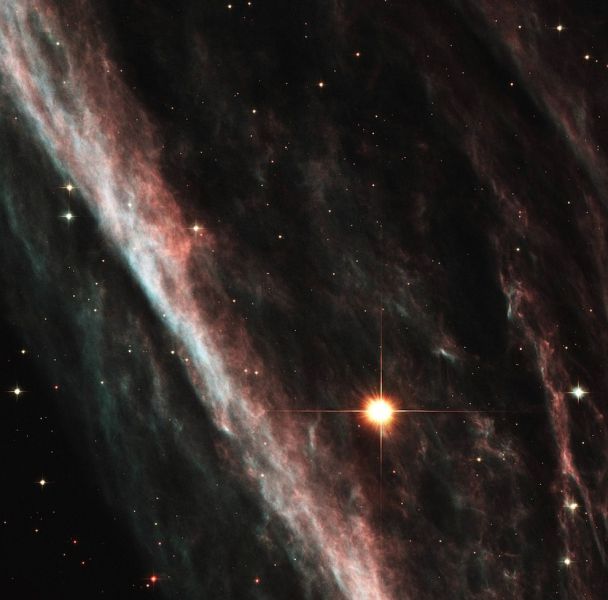

Remnants from a star that exploded thousands of years ago.
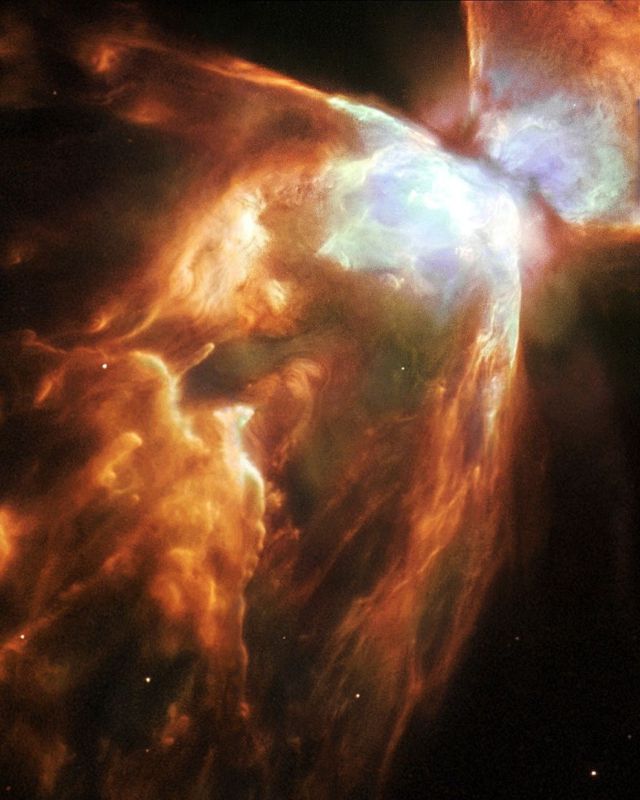

The Bug Nebula (NGC 6302) with impressive walls of compressed gas, laced with trailing strands and bubbling outflows.
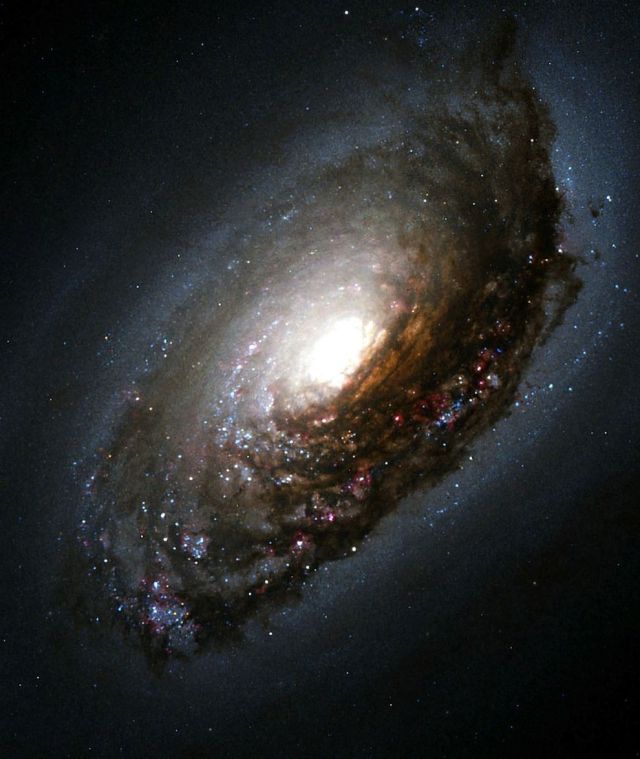

The "Black Eye" galaxy, so named because an ancient cosmic smashup produced a dark ring and a roiling, conflicted interior.
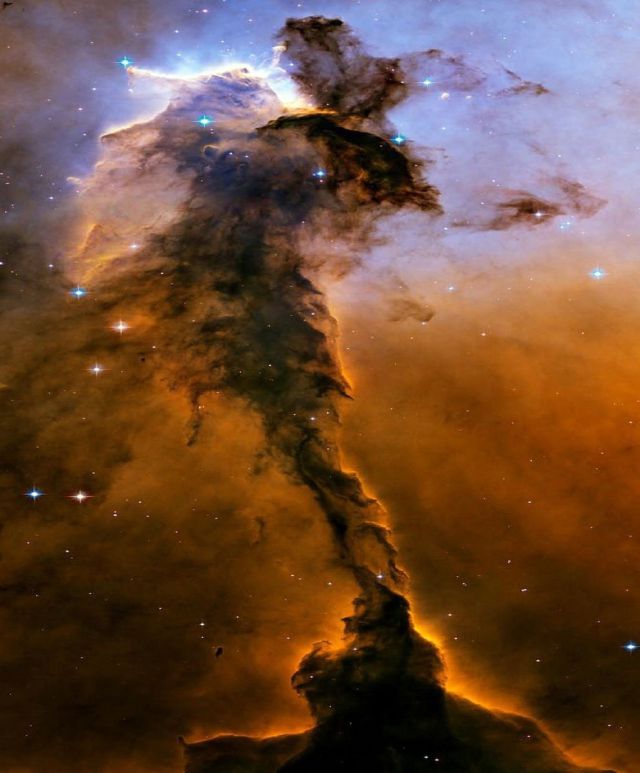

The Eagle Nebula with a tall, dense tower of gas being sculpted by ultraviolet light from a group of massive, hot stars.

The Sombrero galaxy, with stars in a pancake-shaped disk along with a glowing central bulge of stars.
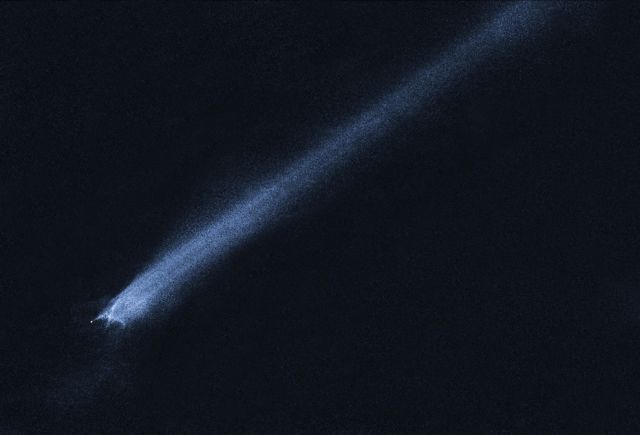

A comet-like object scientists believe was created by the collision of two asteroids, possible siblings of the rogue rock blamed for killing the dinosaurs millions of years ago.
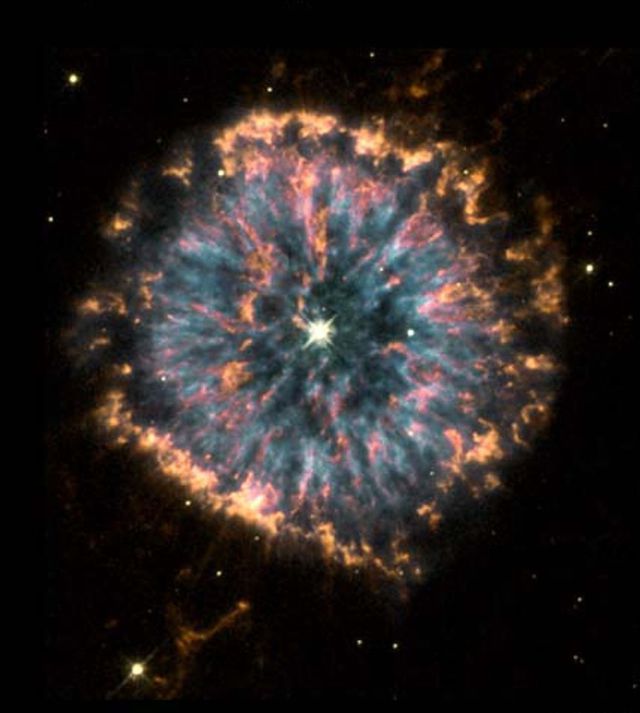

The strikingly unusual planetary nebula, NGC 6751. Glowing in the constellation Aquila like a giant eye, the nebula is a cloud of gas ejected several thousand years ago from the hot star visible in its center.
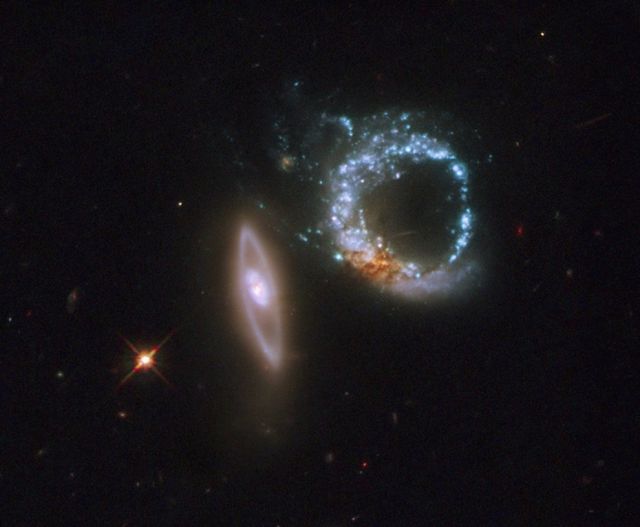
A pair of gravitationally interacting galaxies called Arp 147
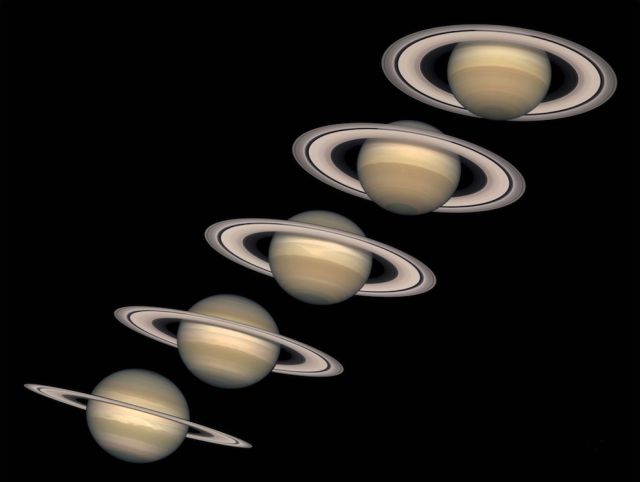

Images of Saturn, shown in a composite photo, captured from 1996 to 2000, depict the planet in different stages of its 29-year journey around the sun.
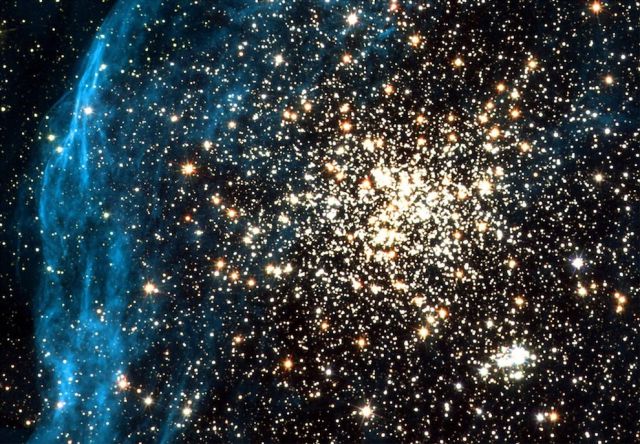

This double star cluster of stars, named NGC 1850, is found in one of earth's neighboring galaxies, the Large Magellanic Cloud.
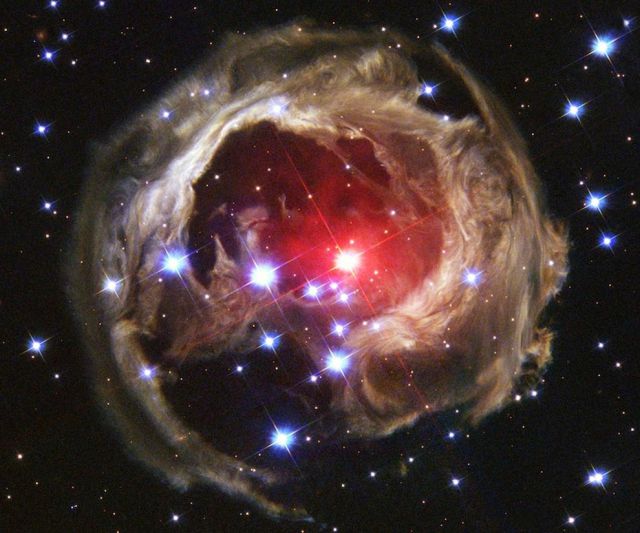

Star V838 Monocerotis's (V838 Mon) light echo, which is about six light years in diameter.

Arp 148 is the staggering aftermath of an encounter between two galaxies, resulting in a ring-shaped galaxy and a long-tailed companion.
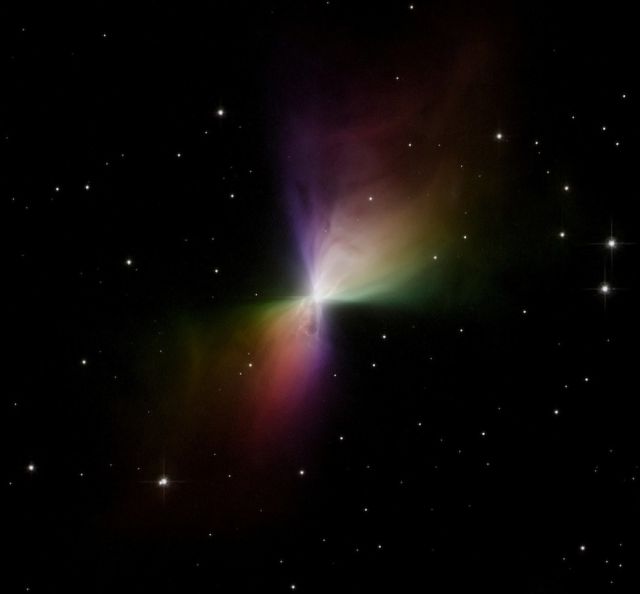

The Boomerang Nebula. This reflecting cloud of dust and gas has two nearly symmetric lobes of matter that are being ejected from a central star.
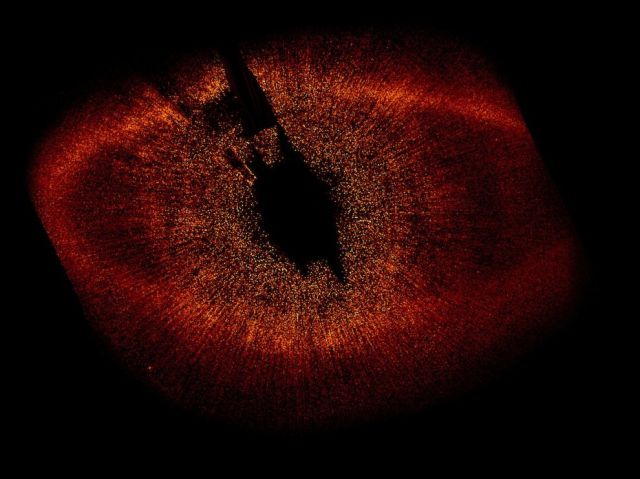
The first visible-light snapshot of a planet circling another star. Estimated to be no more than three times Jupiter's mass, the planet, called Fomalhaut b, orbits the bright southern star Fomalhaut, located 25 light-years away in the constellation Piscis Australis, or the "Southern Fish."
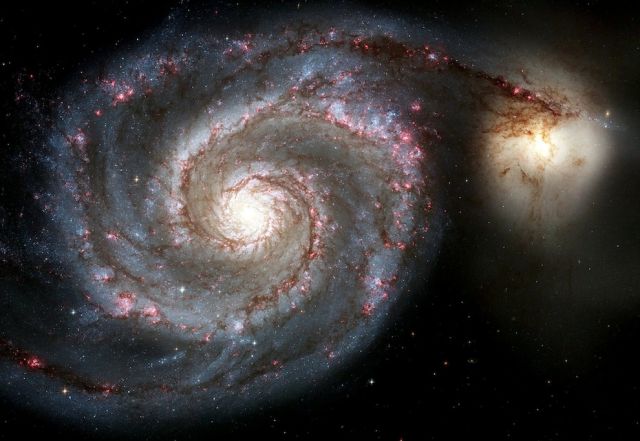

This Whirlpool Galaxy image showcases the spiral galaxy's curving arms where newborn stars reside and its yellowish central core that serves as home for older stars.
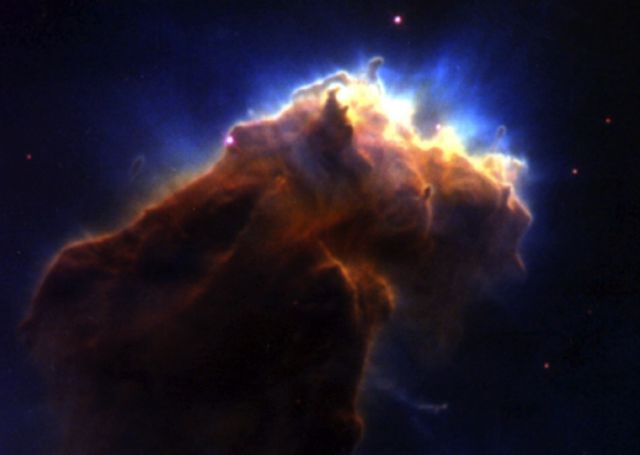

Some stars aren't born, they're hatched from interstellar gas pockets called EGGS (Evaporating Gas Globules) at the end of vast tubes known as "elephant trunks."
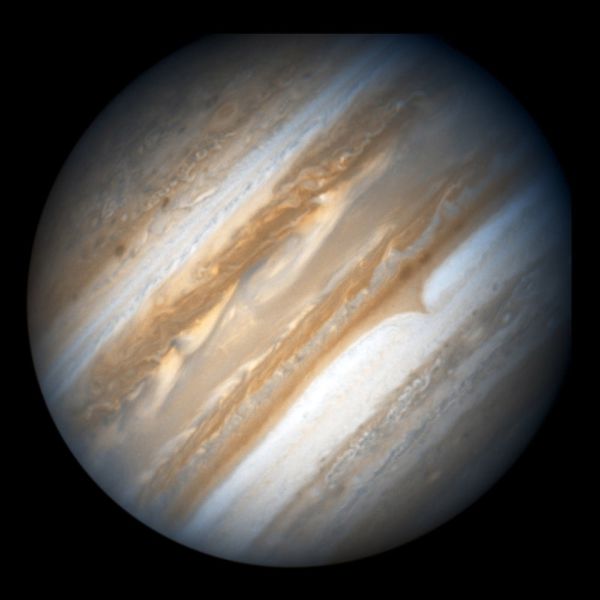

Jupiter's trademark belts and zones of high- and low-pressure regions appear in crisp detail. Circular convection cells can be seen at high northern and southern latitudes.
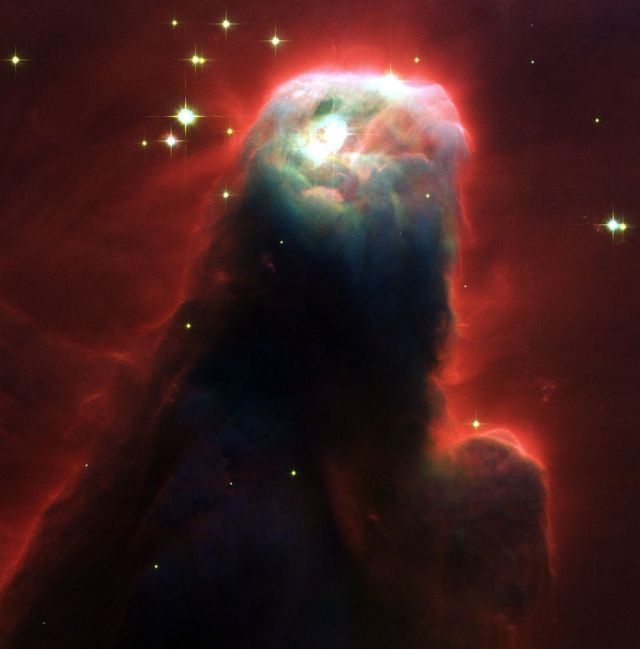

The Cone Nebula, M17. As spectacular as the central subjects of the photographs are, the background is of critical importance to astronomers. What appear as jewel-toned pinwheels, ovals and diamonds on the blackness of space are actually faraway galaxies.
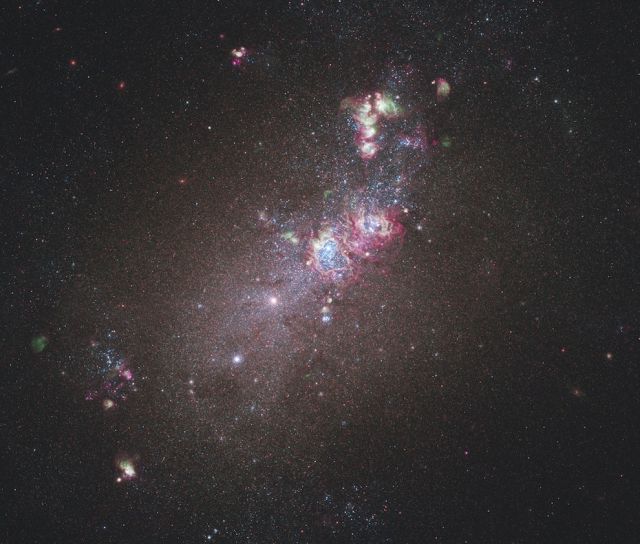

The nearby dwarf galaxy NGC 4214.

A large rare population of hot, bright stars inside the hub of the neighboring Andromeda galaxy.
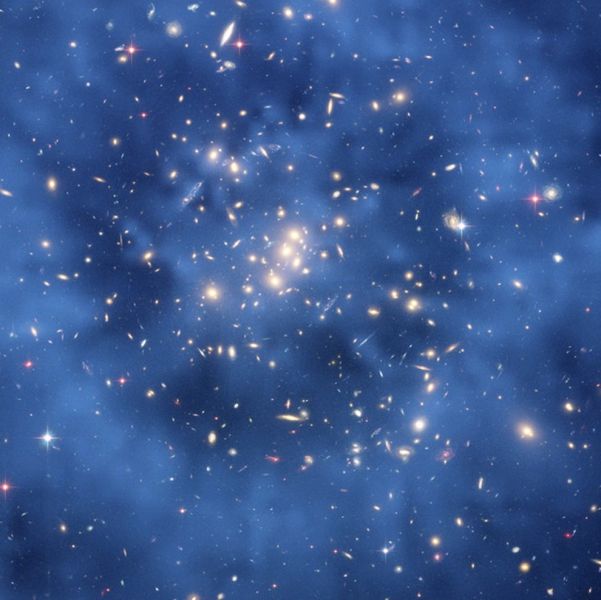

A ghostly ring of dark matter in a galaxy cluster designated Cl 0024+17.
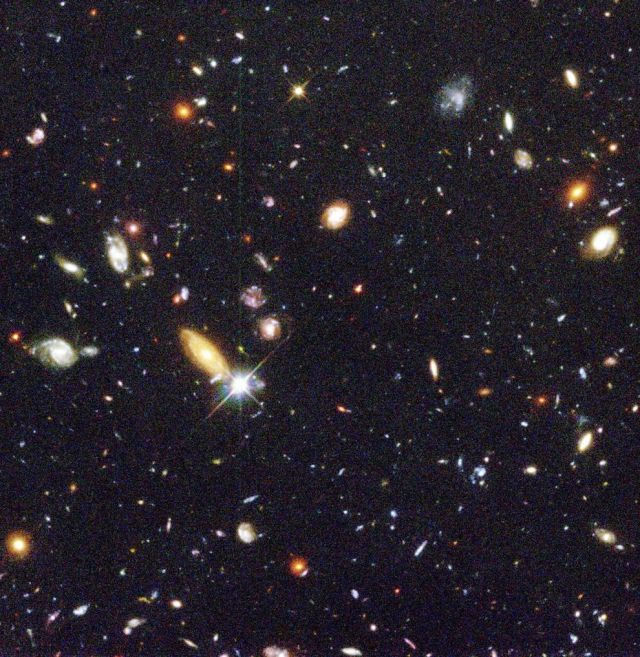

Several hundred never before seen galaxies are visible in this "deepest-ever" view of the universe.
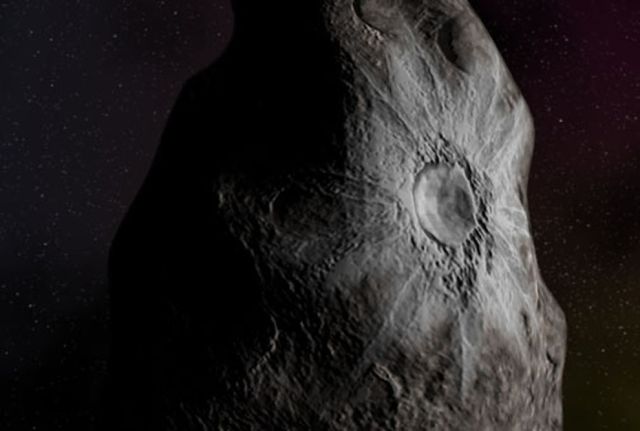

A crater on an object called 8405 Asbolus, a 48 mile-wide chuck of ice and dust that lies between Saturn and Uranus.
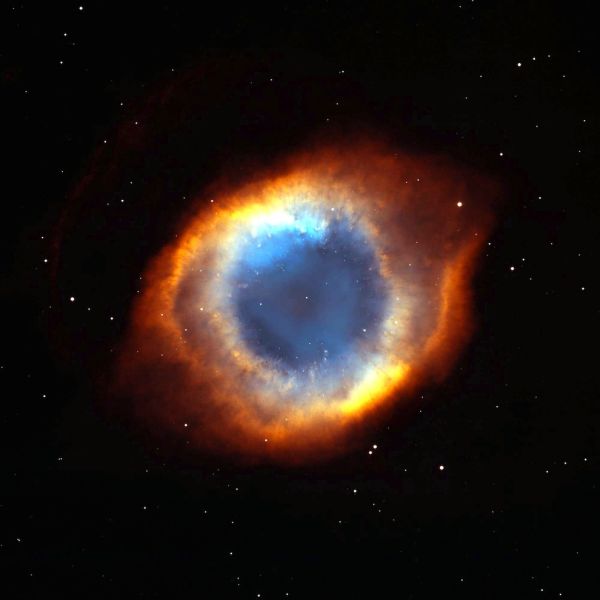
The coil-shaped Helix Nebula.
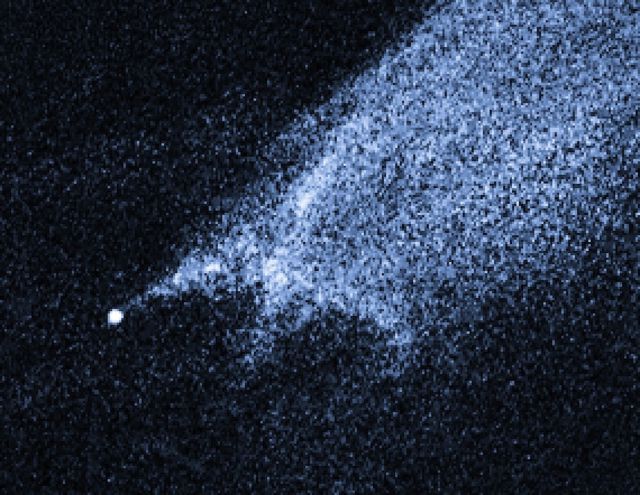

A bizarre X-pattern of filamentary structures near the point-like nucleus of the object and trailing streamers of dust.
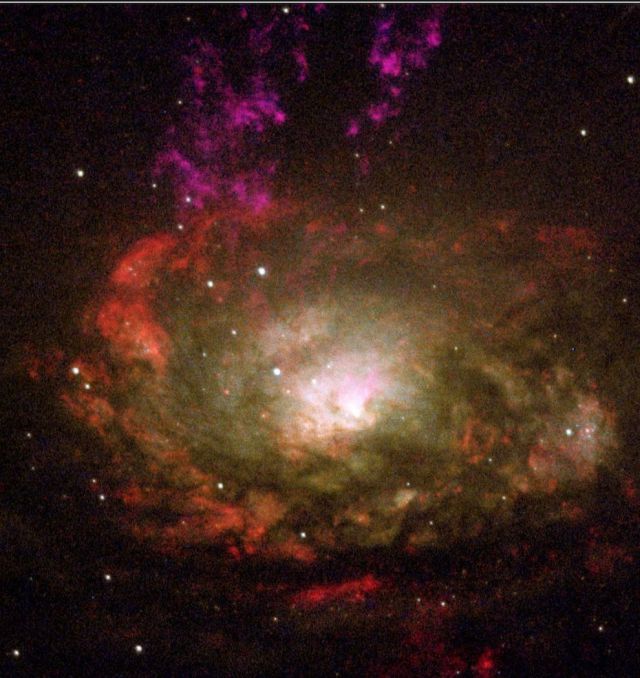

The black hole-powered core of a nearby active galaxy.
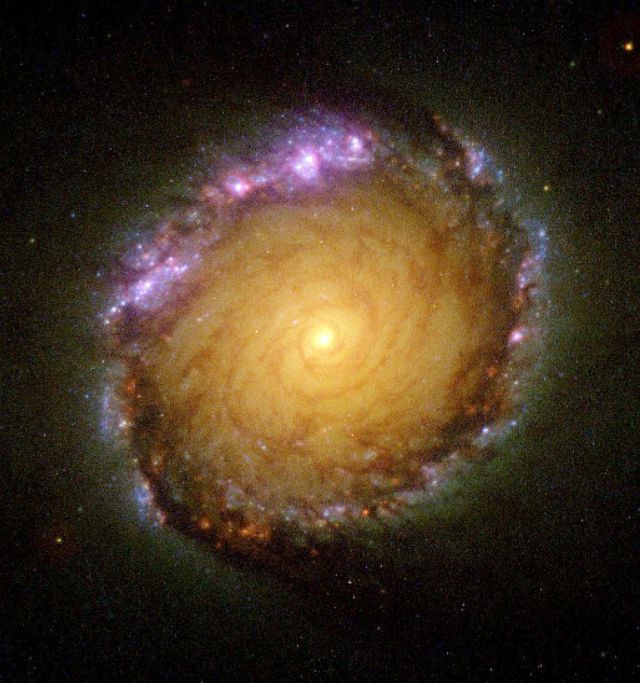

Glowing gold at its center and ringed by a purplish halo, a nearby galaxy holds a vast, stellar nursery with dusty and clean areas for newborn stars.
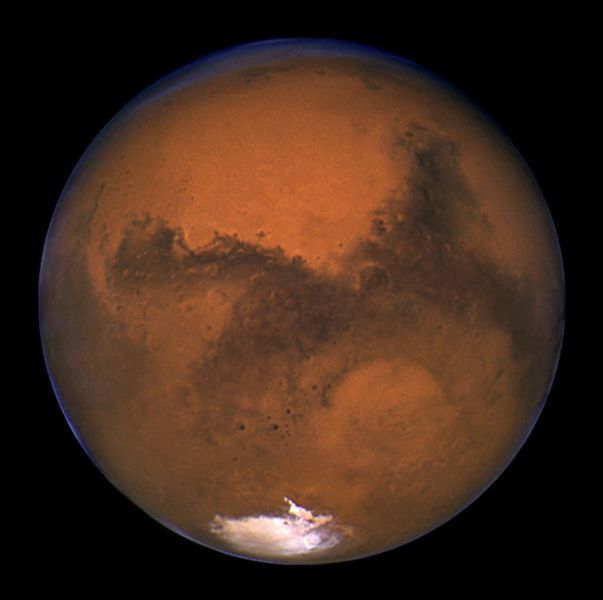

Mars 11 hours before the planet made its closest approach to Earth on August 26, 2003.
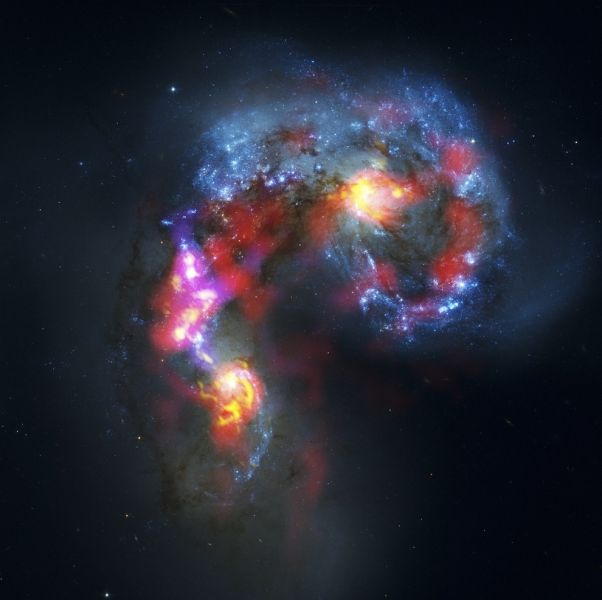

The Antennae Galaxies (also known as NGC 4038 and 4039).
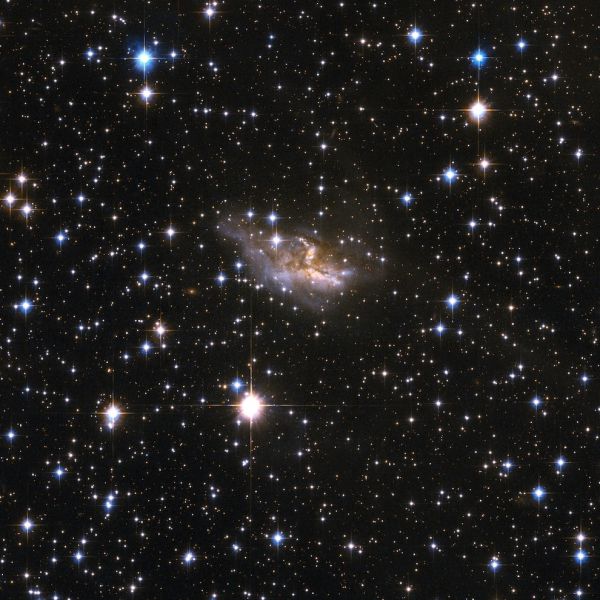

ESO 99-4 is a galaxy with a highly peculiar shape that is probably the remnant of an earlier merger process that has deformed it beyond visual recognition, leaving the main body largely obscured by dark bands of dust.
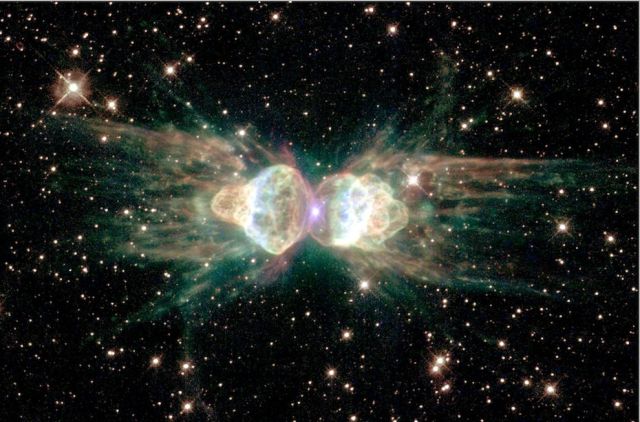

The glowing remains of a dying, Sun-like star known as the "Ant Nebula."
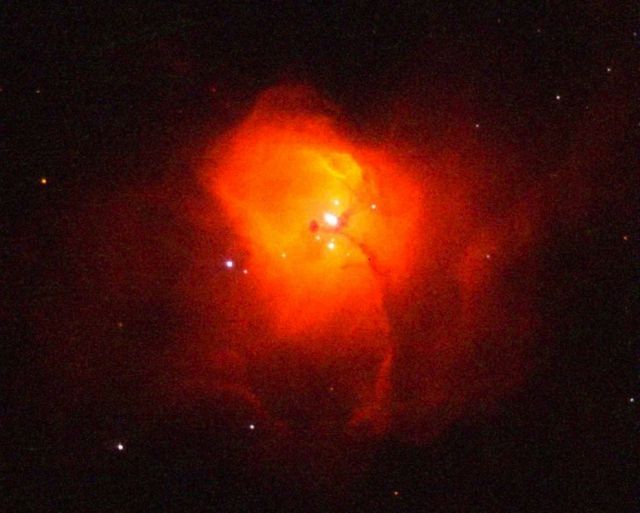

Massive baby stars, nestled in a cloud of glowing gases and shining as bright as 300,000 suns, are at the center of a galactic "family portrait."
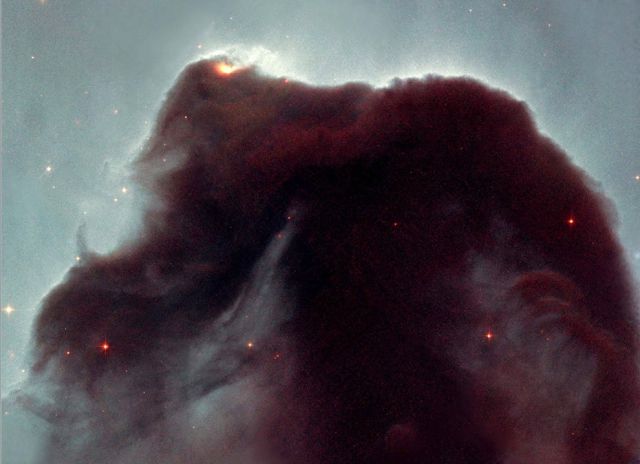

The Horsehead nebula.
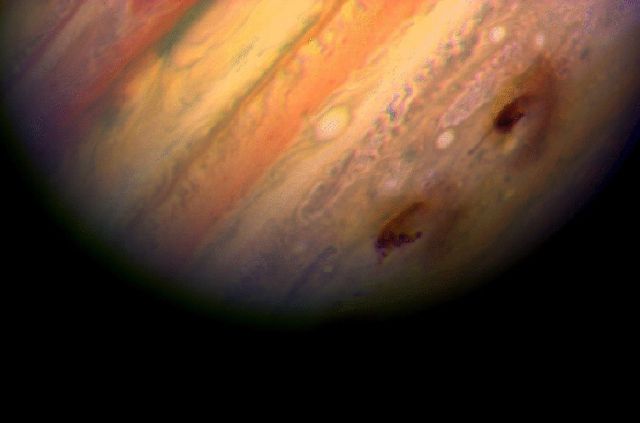

A close-up picture of Jupiter shows the impact site of Fragment G of Comet Shoemaker-Levy 9.
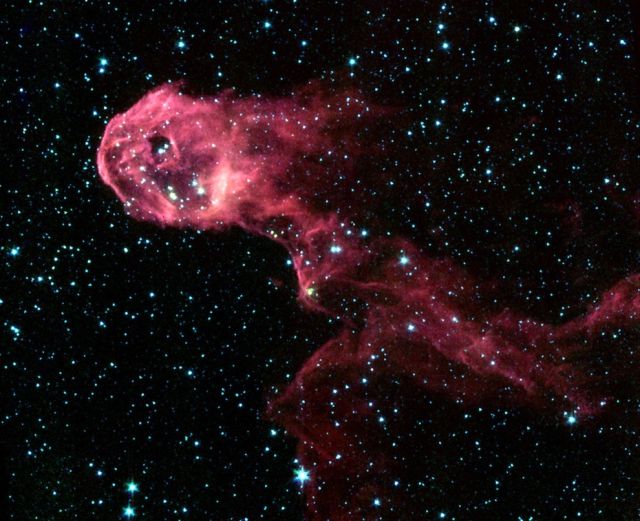

The Elephant's Trunk Nebula, an elongated dark globule within the emission nebula IC 1396 in the constellation of Cepheus.
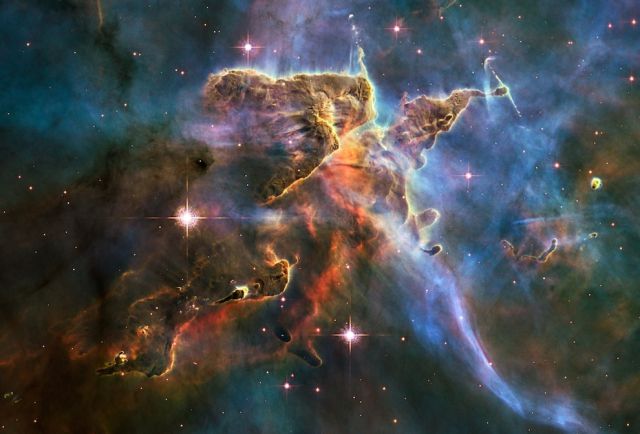

The tempestuous stellar nursery called the Carina Nebula, located 7,500 light-years away from Earth in the southern constellation Carina.
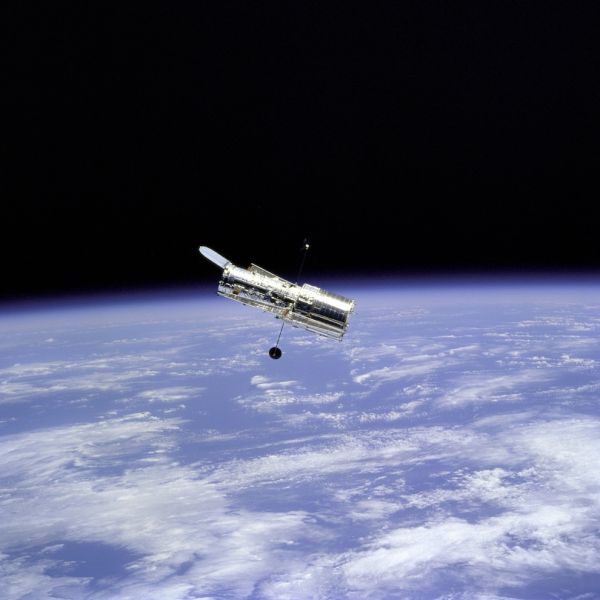

Fly around of the Hubble Space Telescope.
Credits: www.reuters.com

The merging Antennae galaxies. As the two galaxies smash together, billions of stars are born, mostly in groups and clusters of stars.

The massive star Eta Carinae in our Milky Way galaxy that experts believe might explode in a supernova at any time.

A giant star-forming nebula with massive young stellar clusters.

Supernova remnant 0509-67.5, located in the Large Magellanic Cloud, a small galaxy about 170,000 light-years from Earth.

Young, blue star clusters.

The four moons of Saturn passing in front of their parent planet. The giant orange moon Titan casts a large shadow onto Saturn's north polar hood. Below Titan, near the ring plane and to the left, is the moon Mimas, casting a much smaller shadow onto Saturn's equatorial cloud tops. Farther to the left, and off Saturn's disk, are the bright moons Dione and the fainter Enceladus.

Interacting galaxies consisting of NGC 5754, the large spiral on the right, and NGC 5752, the smaller companion in the bottom left.

Remnants from a star that exploded thousands of years ago.

The Bug Nebula (NGC 6302) with impressive walls of compressed gas, laced with trailing strands and bubbling outflows.

The "Black Eye" galaxy, so named because an ancient cosmic smashup produced a dark ring and a roiling, conflicted interior.

The Eagle Nebula with a tall, dense tower of gas being sculpted by ultraviolet light from a group of massive, hot stars.

The Sombrero galaxy, with stars in a pancake-shaped disk along with a glowing central bulge of stars.

A comet-like object scientists believe was created by the collision of two asteroids, possible siblings of the rogue rock blamed for killing the dinosaurs millions of years ago.

The strikingly unusual planetary nebula, NGC 6751. Glowing in the constellation Aquila like a giant eye, the nebula is a cloud of gas ejected several thousand years ago from the hot star visible in its center.
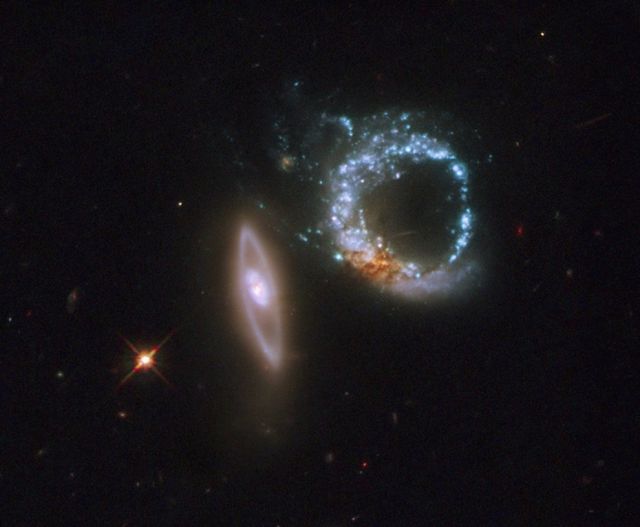
A pair of gravitationally interacting galaxies called Arp 147

Images of Saturn, shown in a composite photo, captured from 1996 to 2000, depict the planet in different stages of its 29-year journey around the sun.

This double star cluster of stars, named NGC 1850, is found in one of earth's neighboring galaxies, the Large Magellanic Cloud.

Star V838 Monocerotis's (V838 Mon) light echo, which is about six light years in diameter.

Arp 148 is the staggering aftermath of an encounter between two galaxies, resulting in a ring-shaped galaxy and a long-tailed companion.

The Boomerang Nebula. This reflecting cloud of dust and gas has two nearly symmetric lobes of matter that are being ejected from a central star.

The first visible-light snapshot of a planet circling another star. Estimated to be no more than three times Jupiter's mass, the planet, called Fomalhaut b, orbits the bright southern star Fomalhaut, located 25 light-years away in the constellation Piscis Australis, or the "Southern Fish."

This Whirlpool Galaxy image showcases the spiral galaxy's curving arms where newborn stars reside and its yellowish central core that serves as home for older stars.

Some stars aren't born, they're hatched from interstellar gas pockets called EGGS (Evaporating Gas Globules) at the end of vast tubes known as "elephant trunks."

Jupiter's trademark belts and zones of high- and low-pressure regions appear in crisp detail. Circular convection cells can be seen at high northern and southern latitudes.

The Cone Nebula, M17. As spectacular as the central subjects of the photographs are, the background is of critical importance to astronomers. What appear as jewel-toned pinwheels, ovals and diamonds on the blackness of space are actually faraway galaxies.

The nearby dwarf galaxy NGC 4214.

A large rare population of hot, bright stars inside the hub of the neighboring Andromeda galaxy.

A ghostly ring of dark matter in a galaxy cluster designated Cl 0024+17.

Several hundred never before seen galaxies are visible in this "deepest-ever" view of the universe.

A crater on an object called 8405 Asbolus, a 48 mile-wide chuck of ice and dust that lies between Saturn and Uranus.

The coil-shaped Helix Nebula.

A bizarre X-pattern of filamentary structures near the point-like nucleus of the object and trailing streamers of dust.

The black hole-powered core of a nearby active galaxy.

Glowing gold at its center and ringed by a purplish halo, a nearby galaxy holds a vast, stellar nursery with dusty and clean areas for newborn stars.

Mars 11 hours before the planet made its closest approach to Earth on August 26, 2003.

The Antennae Galaxies (also known as NGC 4038 and 4039).

ESO 99-4 is a galaxy with a highly peculiar shape that is probably the remnant of an earlier merger process that has deformed it beyond visual recognition, leaving the main body largely obscured by dark bands of dust.

The glowing remains of a dying, Sun-like star known as the "Ant Nebula."

Massive baby stars, nestled in a cloud of glowing gases and shining as bright as 300,000 suns, are at the center of a galactic "family portrait."

The Horsehead nebula.

A close-up picture of Jupiter shows the impact site of Fragment G of Comet Shoemaker-Levy 9.

The Elephant's Trunk Nebula, an elongated dark globule within the emission nebula IC 1396 in the constellation of Cepheus.

The tempestuous stellar nursery called the Carina Nebula, located 7,500 light-years away from Earth in the southern constellation Carina.

Fly around of the Hubble Space Telescope.
Credits: www.reuters.com